After Romney's defeat, the ACA remained in impact throughout of Obama's presidency regardless of Republican efforts to reverse it. In the 114th Congress, Republicans passed an expense that would have reversed much of the ACA, but the expense was vetoed by Obama. After winning the 2016 governmental election, President Donald Trump promised to "rescind and replace" the ACA with a brand-new law.
government, but with 52 seats in the 100-member Senate, Republicans would still have to count on at least some Senate Democrats to overcome a filibuster. Nevertheless, Senate guidelines offer a special budget plan guideline called reconciliation, which enables specific budget-related expenses to bypass the filibuster and be enacted with a basic majority vote.
In 2015, U.S. healthcare expenses were around $3. 2 trillion, or nearly $10,000 per individual typically. Major classifications of expense consist of hospital care (32%), doctor and clinical services (20%), and prescription drugs (10%). U.S. costs in 2016 were significantly higher than other OECD countries, at 17. 2% GDP versus 12.
For scale, a 5% GDP difference represents about $1 trillion or $3,000 per person. A few of the many factors pointed out for the cost differential with other nations consist of: Higher administrative expenses of a personal system with multiple payment procedures; higher costs for the very same product or services; more costly volume/mix of services with higher use of more costly professionals; aggressive treatment of very ill elderly versus palliative care; less use of federal government intervention in pricing; and greater earnings levels driving greater demand for health care.
The 2-Minute Rule for When It Comes To Health Care
There is continuous dispute whether the existing law (ACA/Obamacare) and the Republican alternatives (AHCA and BCRA) do enough to deal with the expense challenge. Both the Republican Politician Home AHCA and Senate BCRA bills have actually proposed major reforms relative to existing law (ACA) that would substantially minimize the variety of persons covered, moderately lower the deficit spending over a decade, reverse the tax increases on the leading 5% (primarily the leading 1%), significantly cut Medicaid payments (25-35%) that benefit lower-income individuals, and broaden option by permitting lower quality insurance to be acquired at lower rates for the young and middle-aged.
States would be allowed more versatility in developing essential health advantages (i. e., insurance coverage policy content). Change tax credit/subsidy formulas used to assist spend for insurance premiums (initially age-based, later modified to income-based) and remove a "cost-sharing subsidy" that decreased out-of-pocket expenses. Supply moneying to health insurance companies to stabilize premiums and promote marketplace participation, by means of a "Long-Term State Stability and Development Program" with functions analogous to a high-risk swimming pool.
Decrease Medicaid payments relative to present law, by topping the growth in per-enrollee payments for non-disabled https://shaneaixt388-07.webselfsite.net/blog/2021/02/12/how-what-might-happen-if-the-federal-government-makes-cuts-to-health-care-spending-can-save-you-time-stress-and-money children and non-disabled adults, by utilizing a lower inflation index. Repeal taxes on high-income earners established under ACA/Obamacare, repeal the yearly charge on health insurance coverage companies, and postpone the excise tax on high premium health insurance (the so-called "Cadillac tax").
young individuals, rather of three times, unless the state sets a different limitation. Eliminate federal cap on the share of premiums that might go to insurance providers' administrative expenses and revenues (the "minimum medical loss ratio"). Public opinion concerning the Republican politician Home (AHCA) and Senate (BCRA) costs was very negative (i.
How To Take Care Of Mental Health for Dummies
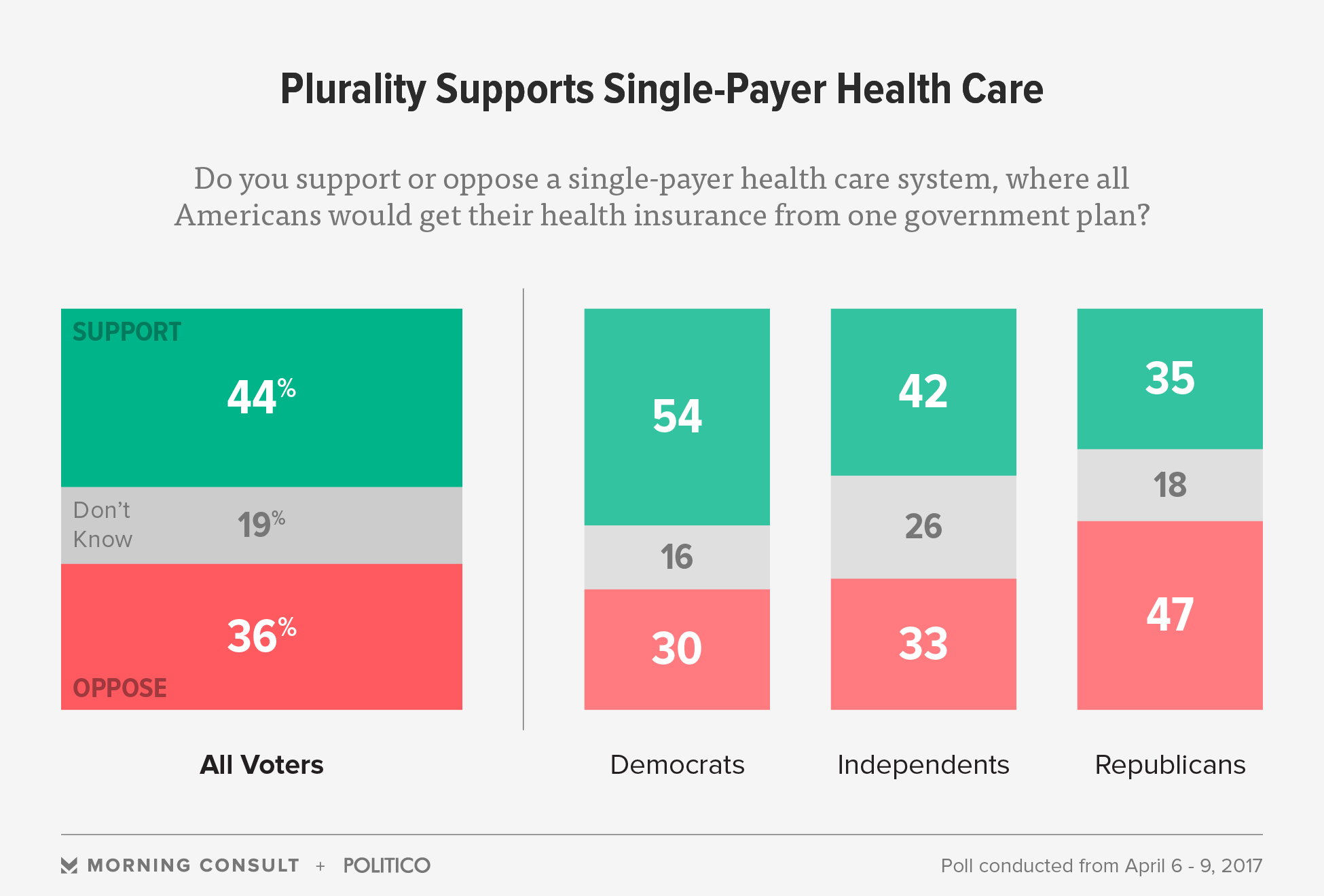
Views were divided along celebration lines. For instance, the monthly Kaiser Family Foundation health tracking survey for Might 2017 indicated that: More view the Republican AHCA unfavorably (55%) than favorably (31%). Views are divided along party lines, with % in favor of AHCA: Democrats 8%, Independents 30%, Republicans 67%. Although historically more people saw the existing law (ACA/" Obamacare") unfavorably than favorably, in Might 2017 more had a beneficial view (49%) than undesirable (42%).
Health care professionals from throughout the political spectrum liberal, moderate, and conservative concurred that your house Republican politician healthcare costs was impracticable and suffered from fatal flaws, although specific objections differed depending on ideological point of view (what is a single payer health care). Experts concurred that the expense fell far short of the objectives laid forth by President Donald Trump throughout his 2016 campaign "Economical coverage for everybody; lower deductibles and healthcare costs; better care; and no cuts to Medicaid" due to the fact that the expense was (1) "almost certain" to minimize overall health care coverage and increase deductibles and (2) would phase out the Medicaid expansion.
CBO approximated in Might 2017 that under the Republican AHCA, about 23 million less people would have health insurance in 2026, compared with present law. AHCA (Republican health care expense) effect on income distribution, since the year 2022. Net advantages would go to families with over $50,000 earnings on average, with net expenses to those below $50,000.
Cuts to Medicaid more than balanced out tax cuts, resulting in moderate deficit reduction. Changes in Medicaid Costs Under the Better Care Reconciliation Act Compared to CBO's Extended Baseline Share of Nonelderly Grownups Without Medical Insurance Protection Under Current Law and the Better Care Reconciliation Act, by Age and Income Classification, 2026 CBO forecasts of individuals without medical insurance under 65 years of age (%) under various legal proposals and current law.
The smart Trick of What Is The Republican Health Care Plan That Nobody is Discussing
e., the actuarial worth, or percent of costs an offered policy is expected to cover). Other groups have actually examined a few of these aspects, along with the distributional impact of the tax modifications by earnings level and effect on job development. The results of these analyses are as follows: According to each of the CBO scores, passage of the Republican bills would lead to a significant decrease in the variety of individuals with health insurance, relative to current law.
In 2018, the majority of the reduction would be triggered by the removal of the penalties for the private required, both directly and indirectly. Later decreases would be because of decreases in Medicaid enrollment, elimination of the private mandate penalty, subsidy reduction, and greater expenses for some individuals. By 2026, an approximated 49 million people would be uninsured under the Senate BCRA, versus 28 million under current law.
According to White House Communications Director Michael Dubke, the analysis tried to use comparable methodology as the CBO. Other individuals and organizations such as the Brookings Institution and S&P approximated sizable coverage losses due to the AHCA. According to a report published by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, the legislation would result in 3 million more children (defined as persons under 18 years old) losing healthcare coverage.
Approximately $1. 2 trillion less would be spent over that time, while $900 billion less in tax income would be collected. Medicaid spending would be cut substantially. Taxes on the approximately top 5% of income-earners under present law would considerably drop. CBO AHCA Modified March 24: In settlements after the initial report, the law was customized such that the CBO approximated the deficit reduction would amount to about $150 billion over a decade.
3 Simple Techniques For How Long Does Medicare Pay For Home Health Care?
For scale, CBO has actually estimated that the U.S. will add roughly $9. 4 trillion to the debt total over the 2018-2027 duration, based on laws in location since January 2017. The $321 billion therefore represents a reduction of about 3. 5% of the total financial obligation boost over the decade, while the $150 billion has to do with 1.